Linear Structures
Linear Structures. Stacks and Queues
Definition
With most data structures, adding and removing values causes the system to grow or shrink. However, linear structures change shapes in a planned way: they release points according to how they added them.
Interface
Linear structures abide by a simple interface:
public interface Linear<E> extends Structure<E>{
// value is non-null
// value is added to the collection
// the consistent replacement policy is not specified
public void add(E value);
// structure is not empty
// returns reference to next object to be removed
public E get();
// structure is not empty
// removes an object from store
public E remove();
// returns number of elements in structure
public int size();
// returns true iff the linear structure is empty
public boolean empty();
}
The add and remove methods are used to:
i. insert new values into the linear structure
ii. remove those same values later
Types of Linear Structures:
In the following, we discuss two different linear structures:
I. Stacks: an ordered collection of items with the behavior that the last item in is the first item out.
II. Queues: an ordered collection of elements with, unlike a stack, the first item in is the first item out.
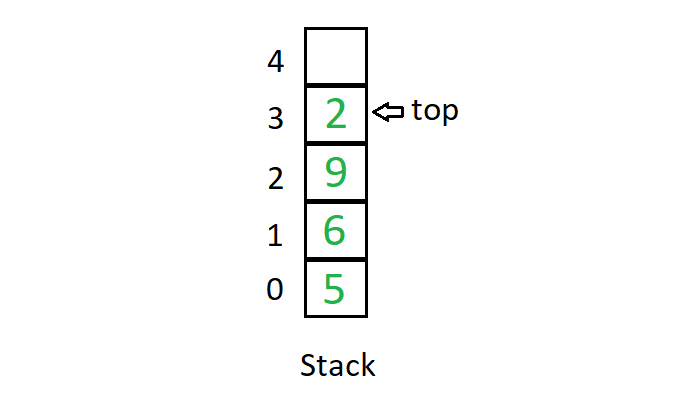
Stacks
Definition
A stack is a collection of items following the behavior that the newest inputted value is the first item to be removed.
Methods
i. The add method pushes an item onto the stack, while remove pops off the item that was pushed on most recently.
ii. methods push and pop are alternatives for add and remove, respectively
Interface
Here is the interface that defines what it means to be a Stack:
public interface Stack<E> extends Linear<E>{
// item is added to stack
// will be popped next if no intervening push
public void add(E value);
// item is added to stack
// will be popped next if no intervening push
public void push(E value);
// stack is not empty
// most recent added item is removed and returned
public E remove();
// stack is not empty
// most recent pushed item is removed and returned
public E pop();
// stack is not empty
// top value (next to be popped) is returned
public E getFirst();
// stack is not empty
// top value (next to be popped) is returned
public E get();
// stack is not empty
// top value (next to be popped) is returned
public E peek();
// returns true iff the stack is empty
public boolean empty();
// returns the number of elements in the stack
public int size();
}
Queues
Definition
A Queue is an ordered collection of elements with tightly controlled access. Unlike the stack, the initial value entered first is the first item to be deleted.
Methods
The primary operations of queues are to enqueue and dequeue elements.
i. The program adds elements to the rear; the data points then pass through the structure, eventually reaching the head, where the program removes these data points.
ii. To support the linear interface, we supply the alternatives methods: add and remove
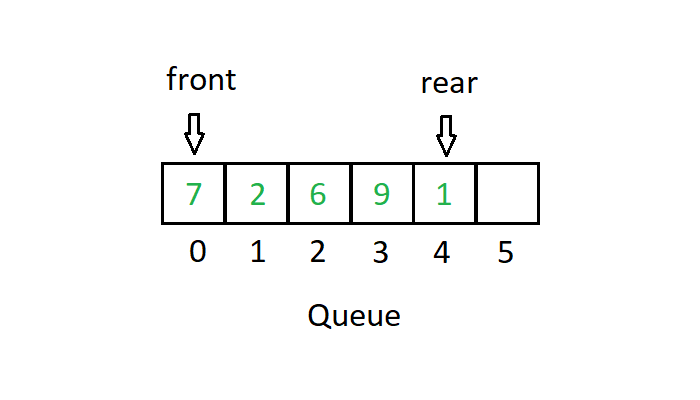
As elements are added (enqueued), the Queue expands the Vector; as elements are removed, the leftmost element is removed, shrinking the Vector.
Interface
The interface provides a number of other features we have seen already:
public interface Queue<E> extends Linear<E>{
// value is added to the tail of the structure
public void add(E value);
// value is added to the tail of the structure
public void enqueue(E value);
// queue is not empty
// head of the queue is removed and returned
public E remove();
// queue is not empty
// head of the queue is removed and returned
public E dequeue();
// queue is not empty
// element at the head of the queue is returned
public E getFirst();
// queue is not empty
// element at the head of the queue is returned
public E get();
// queue is not empty
// the element at the head of the queue is returned
public E peek();
// returns true iff the queue is empty
public boolean empty();
// returns the number of elements in the queue
public int size();
}
Summary
Operations
The linear structures Stack and Queue each implement add and remove operations. a. Typical implementations of Stacks refer to these operations as “push” and “pop”
b. Typical implementations of Queue methods refer to these operations as “enqueue” and “dequeue”
Linear Interface
i. These structures solve similar search problems; accordingly, they share a comparable linear interface.
ii. a common interface allows us to freely swap implementations